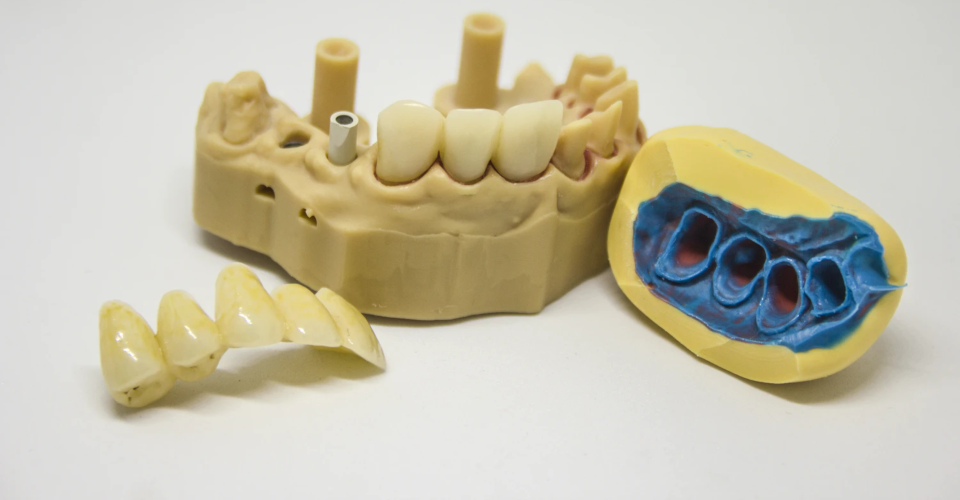
Dental 3D Printer: Reshaping Dentistry
Dentophobia: a Fear of the Dentist. According to statistics, about 75% of adults in the United States experience a certain amount of fear associated with dental visits; 5 to 10% are strong enough concern to be considered dentophobia.
This may not come as a shock since going to the dentist’s office back in the old days can indeed be traumatizing in one way or another.
Much has changed since the introduction of 3D printing technology in dentistry. Today, 3D printers are standard in dental clinics and laboratories because they allow oral healthcare professionals to deliver better products and services to their patients.
Once considered as a dreaded visit is now something a growing number of individuals look forward to.
3D printing technology has resonated in the dental field since it cuts down traditional dentistry’s tedious and lengthy procedures. Before, patients need several trips to their dentist’s clinics and even endure temporary fixes. With the latest advancement of 3D technology, same-day dental practices are now possible, safer, and more effective.
What is Dental 3D Printing
3D Printing is denoted to as an additive manufacturing (AM) process that fabricates tangible objects from digital files. You can see it in almost every industry you can think of.
In dentistry, 3D printing works hand-in-hand with CBCT scanners and CAD software to create detailed replicas of the patient’s oral cavity. The printed model is used to produce guides for dental implants and surgeries and fabricates oral prostheses.
3D printing also plays a role in rapidly prototyping instruments for dental surgeries or any mundane devices that dentists use in their daily practice. These 3D printer innovations have led to the development of new dental procedures and approaches.
Dental 3D Printer Technologies
As stated, AM has infiltrated almost every industry we can think of, and dentistry is not an exception. Here are a few examples of medical technologies used by dentists with the aid of 3D printers:
Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA) uses a UV laser beam over a correct x and y coordinates to induce polymerization of a photosensitive liquid. Then, this hardens and transforms it into a polymerized solid. To simplify, SLA uses a light source to cure a specific area in a tank of liquid resin to turn it into hardened plastic.
SLA 3D printing has been around as early as the 1970s. However, it had only gained popularity at the end of the 2000s when patents began to expire. The introduction of small-format 3D printers broadened the access of additive manufacturing to the public.
Dental models made using stereolithography are a favorite because of their durability, higher resistance to temperature, lower moisture absorption, and the possibility of shrinking. These clinical models aid health professionals in diagnosing, pre-operative planning, implant design, and manufacturing dental prostheses.
Digital Light Processing

Digital Light Processing (DLP) has a similar process with SLA, except it uses a conventional light source from a projector to cure liquid resins. Unlike SLA, the whole tank of liquid wax is bare to the UV light. DLP machine operators can control the intensity of the UV light source. Its UV light source is less expensive. Plus, you can easily replace it.
DLPs are more effective in printing large parts with only a few details and building one-off small and intricate parts. Depending on the model, DLP generally produces objects with higher detail resolution.
Material Jetting
Material Jetting is also known as PolyJet and MultiJet Modeling. This type of 3D printer works just like our inkjet printers. However, instead of ink dropping on paper, the machine jets layers liquid resin on a built-in tray and is instantly cured with UV light.
For years, material jetting was the most commonly used 3D printing technology used in the dental industry since its system has high throughput. But with the extensive post-processing required, it generally became inferior to SLA and DLP.
Choosing the Right 3D Printer
The continuous innovation with 3D technology has resulted in different types and models of 3D printers. 3D printers are made differently, which is why dental practitioners should take note of the three technologies commonly used in 3D dentistry, which we have mentioned earlier.
In addition, it is always important to first evaluate the capacity and specification of the printer before investing in one. Here are five critical factors that you should carefully consider when choosing the right printer for your office:
Accuracy and Precision
Many mix up the concept of accuracy and precision. For clarification purposes, accuracy is the degree of closeness to an actual value, while precision refers to the repeatability or consistency of the measurement.
As an additive process, 3D printers fabricate objects by building them layer by layer. Each layer may pose a possibility of inaccuracy, and every layering process affects the level of precision.
Dentists give utmost importance to accuracy when it comes to giving their patients proper dental care. Teeth replica and other dental prostheses must be accurately completed to fit the patients perfectly and prevent further complications. For this very reason, it is key to consider the accuracy and precision of 3D printers for digital dentistry.
Ease of Use
Machines are invented to make out tasks easier. However, it is indisputable that there are some technologies out there that are complicated to operate. When choosing a 3D printer, select one with easy-to-use software that is still very configurable and powerful.
A lot of oral healthcare workers have adopted digital technologies to simplify their workflow and production processes. 3D printers have eliminated several methods, such as thermoforming and product trimming, thus saving dentists and lab technicians’ time, labor, and materials.
Cost and Return of Investment (ROI)
Many still question if 3D printers are worthy investments or just a waste of money. For small offices, acquiring a 3D printer may be costly. Thus, there are still some who prefer outsourcing processes that require this machine. Today, though, we can see many reasonably priced 3D printers in the market that are investment-worthy, specifically if you will be using them for business purposes.
A logical step when buying a 3D printer – or anything for this matter – is to calculate your finances and consider the following factors:
- Initial cost (machine and software, machine setup, training)
- Operating cost (how much your per-unit material will be)
- Maintenance and Servicing Costs
With these in mind, you will be able to calculate your ROI. If bringing dental lab work in-house saves more cost, it is high time to purchase a 3D printer for your clinic. Make sure that the printer you’re eyeing will not only maximize your investment but will also give you profit.
Today you can find professional desktop 3D printers for around 6,000 USD without compromising the machine’s speed and accuracy.
Materials

The materials you use for 3D printing is critical since it affects the machine’s performance and quality of the end product. Although most 3D printers are compatible with almost any type of materials, some printers are specifically designed for a particular raw material.
Most dental clinics and laboratories use resin as materials for oral prostheses and are removable. They are primarily designed and manufactured for the production of dental appliances and models.
Print Speed
When we put out the inkjet printer in draft mode, it will print our file rapidly. But when we set it on high quality, printing a file would be slower. Printing speed, however, is often inversely proportional to the end quality of the product. This means that the faster the completion, the lower the quality.
Most 3D printers can support three types of printing speed: 40 to 50 mm/s, 80-100 mm/s, and 150 mm/s. Since accuracy and precision is very important in dentistry, the end product should be of top quality. Choose a printer with a speed that will not affect the resolution and accuracy of your end product.
Applications of Dental 3D Printers
Dentistry has several branches, just like the medical field. Today, dental practitioners and laboratories are using 3D printers for a wide variety of applications. Here are some of the examples of how 3D printers are applied in different dental practices and procedures:
Pediatric Dentistry, as its name suggests, focuses on giving oral treatment to kids and teens. This age group, in general, have shorter patience and lesser pain tolerance than adults; hence, it is vital to make dental appointments as quickly as possible. With 3D scanning and printing, treatments are not only faster but also more friendly and comfortable.
Periodontics is a dental branch that focuses on the inflammatory disease that destroys the teeth’ gums and other supporting structures. 3D printers fabricate the scaffold during periodontic procedures for socket preservation, periodontal repair and regeneration, and sinus and bone augmentation.
Using surgical templates from 3D printers during implant placement increases accuracy and reduces deviation, significantly minimizing the chances of complications post-procedure.
Endodontics concerns the dental pulp and tissues surrounding the roots of a tooth. The most common procedure performed in endodontics is the root canal, which we all know can be pretty painful.
Many dentists these days use 3D printed guides to assist them in accessing the root canals with damaged pulp tissue. Aside from providing more accurate results, these guides also reduce treatment time and make the procedure less painful and traumatizing.
Prosthodontics is a dental specialty that diagnoses, treats, rehabilitates, and maintains the patient’s oral function. Over the years, prosthodontic treatment has been sought after by individuals for aesthetic purposes.
3D printing technology delivers a broad range of applications in the works of dentists by helping them fabricate more precise and accurate dentures and implants for their patients.
Benefits of Using Dental 3D printers
Easy Customization
Dental indications should be patient-specific to match the anatomy of the individual. Thus, dentistry requires high levels of customization. Traditional methods rely on manual or semi-mechanized techniques to create dental prostheses, resulting in poor quality and inaccuracy. In addition, some processes are even outsourced from third-party shops and would take at least a week to complete.
Today, digital workflows enable mass customization in a consistent, automated way, requiring less labor and incurring lower costs. 3D scanners can easily take an image of your oral cavity from all angles. Using CAD software, the technician uses the pictures to pattern a 3D model of your teeth and jaw to fabricate your prostheses using a 3D printer.
The advantage of digital dentistry is that professionals can keep the images in a virtual library and easily make some corrections when necessary.
Implants
Prosthodontists use 3D scanners and printers to create an accurate guide for dental implant procedures. By doing so, they have better control of the entire, minimizing human errors.
3D printed implants are also more precise and accurate compared to those conventionally made. They are compatible with the surrounding bone and gum tissues and reduce the chances of bruising, swelling, and post-operative complications.
Dentures
The traditional way of making dental dentures – may it be permanent or removable –involves several processes. One of these is creating a surgical guide that fits over the existing teeth and gums of the patient. Conventionally, dentists would use plaster casts to get a mold of your oral cavity and make your dentures.
Today, most patients do not need to get those icky gunk in their mouth because 3D scanners can easily take images of your teeth and mouth and have the patterned model 3D printed. If your oral health care provider has a 3D printer in the office, you can have your dentures printed within an hour, depending on the speed of the machine.
Patient Experience
As mentioned earlier, there is a large percentage of adults in the US with a certain level of fear related to dental visits. This is most probably due to a traumatic experience during their childhood days when you need to keep your mouth wide open while the dentist probes the insides with different pointed tools.
Today, thanks to 3D scanners and printers, dentists can now easily create models of their patient’s problem areas to help them give the proper diagnosis and treatment. In addition, the technology also eliminates redundant steps. As a result, dental procedures are now faster, more accurate, and less invasive; thus, making clinic visits less upsetting.
Final Thoughts
3D Dental Printing is the key to modern dentistry. It has many applications, from creating models for study and surgery guides to fabricating patient-specific oral dentures and prostheses. In general, it has made their routine practice a lot easier.
There are several types of 3D printing technologies, but SLA, DLP, and Material Jetting are the three most commonly used by the dental industry. The technologies are all effective in fabricating 3D objects for orthodontic purposes but have their pros and cons. Thus, it is crucial to consider several factors such as the printer’s speed, accuracy, the materials you will be using, and ease of handling before purchasing one.
3D printers are flexible when it comes to materials used. But since orthodontic works are unique and patient-specific, dentists and lab technicians use dental resins to fabricate dental models.
By application 3D technology, dental treatments and procedures are now faster and more reliable. Prostheses are more precise and accurate, making them more compatible and comfortable for the patients to wear.
In addition, 3D printing significantly reduces complications after procedures and improves the overall patient experience.
As 3D printing improves, many people still wonder if 3D technology will eradicate traditional dental practices. This is not the case. 3D dental printing is, in fact, just a new way of doing the conventional procedures but only quicker and generally better.
Because of this, you will see new materials and technology that will fulfill dental requirements. Who knows, there might be entirely 3D printed teeth in the future.