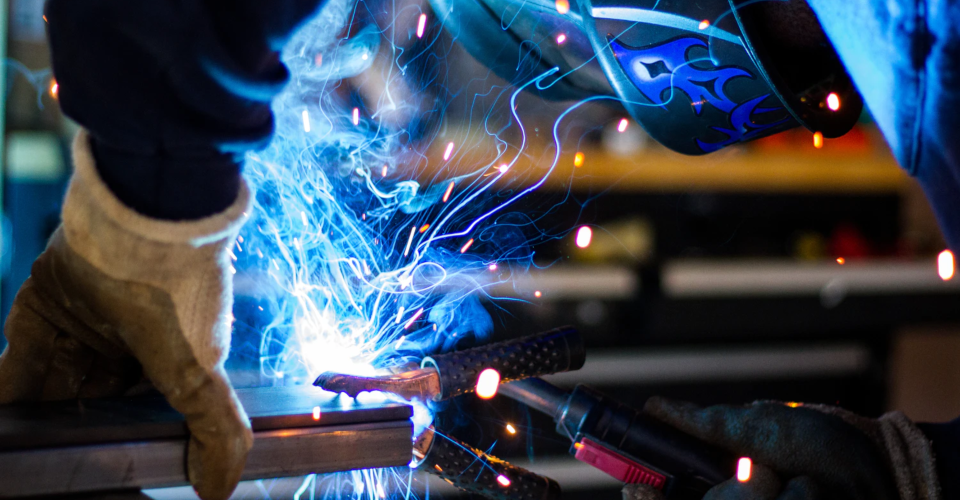
Which Industries Use Fiber Lasers?
Although a lot of people have probably heard of laser technology at some point in their lives (and used it, even without them knowing it), it’s rarely discussed how there are different types of lasers. Even in the field of manufacturing industries that use lasers, different types of lasers are used for different applications and materials.
In this article, we’re drilling down on this topic and focusing on fiber lasers. Compared to other types of lasers, fiber lasers are quite new. Within that short period of time, a lot of industries have found themselves adopting the use of fiber lasers because of its unique properties. How are fiber lasers being used nowadays?
What is a fiber laser?
As the name implies, a central component of a fiber laser is a fiber-based delivery system. This flexible material also doubles as the laser’s active gain medium and is doped by rare-earth elements typically erbium, neodymium, or ytterbium.
The unique design of fiber lasers gives them a very high optical gain and a high surface area to volume ratio. In the same way that fiber optics can deliver a signal for thousands of miles, the reach of fiber lasers can also be extended to vast distances.
In the manufacturing industry, the use of fiber lasers has allowed laser cutting and engraving machines to have more compact designs. This is because fiber lasers can be bent and coiled in ways that were not possible with other laser types. Despite the smaller footprint, fiber laser machines are just as powerful and can even more energy-efficient than their larger counterparts.
Benefits of fiber lasers
High efficiency
The use of a fiber-based gain medium in fiber lasers makes them a lot more power-efficient compared to gas lasers. Put simply, this means that fiber lasers can output higher power from the same input. Lower power requirements will then lead to reduced operating costs, especially for large-scale manufacturing facilities. The high peak power of fiber lasers also means that they can cut at faster rates and produce cleaner cuts.
Low maintenance requirements
In the manufacturing industry, fiber lasers are what is known as an example of a ‘fit and forget’ technology. Practically, all lasers used for cutting and engraving are pretty low-maintenance, but fiber lasers take that advantage up several notches higher. Even if a fiber laser needs to be maintained or repaired, the associated costs are typically still lower compared to gas lasers.
Wider versatility
The large optical gain of fiber lasers makes capable of outputting higher-powered laser beams, which means that they can cut through materials that gas lasers cannot. Because of this, fiber lasers are the more preferred technology for engraving or cutting through metals. With a fiber laser, it is even possible to “drill” through thick metal by sending continuous pulses of laser on a single spot of the workpiece.
Smaller footprint
Fiber laser machines are well-suited to facilities with limited space. Compared to machines that use gas or solid-state lasers, fiber laser machines are typically smaller. This compact design is possible because of the use of a flexible fiber-based gain medium.
Most industry experts would consider making the transition from gas-based laser to fiber lasers an ‘upgrade.’ From the benefits of fiber lasers that we have seen so far, this is more than just a marketing slant. As fiber lasers become more common, we can expect the transition from older laser technology to become easier for most industries.
Industries that use fiber lasers
Fiber lasers are especially suited to working with metals, so it’s no surprise that industries that revolve around metal parts have become the primary users of this new laser technology. Just to give a sampling of how useful fiber lasers currently are, here are just a few major industries that have used fiber laser technology to augment their processes.
Automotive industry

The automotive industry has turned out to be one of the most significant users of fiber laser technology, especially in an era where increased throughput is something that car manufacturers strive for. Lasers have proven to be useful in just about every stage of automobile manufacturing – from the differential gears in a car’s transmission system to the foils used to coat its batteries
The high efficiency of fiber lasers has certainly become crucial for automotive manufacturers. With such a high-volume demand, the savings in power costs – up to 50%, in some cases – have made making the transition to fiber lasers well worth the initial investment.
Medical industry

In the medical industry, the use of lasers is less about its power efficiency and is more interested in how safe and accurate the technology is. Since fiber lasers can work with metal, they are ideal for creating extremely precise surgical tools like drills, bone saws, and scalpels. Fiber lasers can also be used to make marks in stents or implants that are safe for the human body and will not be erased when placed in contact with bodily fluids.
The use of laser marking in lieu of traditional methods for creating implants and medical tools have made the process faster and cheaper and has helped make healthcare accessible to more people.
Jewelry making
![]()
While wooden jewelry cut by gas lasers are nice and cheap, they don’t quite have the same level of luxury as jewelry made from silver or gold. Fiber lasers have revolutionized the art of jewelry making, giving craftsmen a tool for creating pieces at a previously unattainable degree of precision. The high control that fibers lasers offer makes them useful not just for cutting of pieces, but also for customized marking and engraving. There’s also the fact that fiber lasers are non-contact – a crucial factor when handling delicate and precious metals.
Electronics
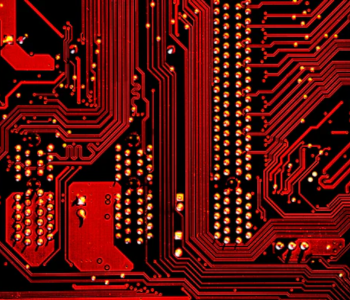
As time progresses, we have seen electronic devices get smaller and smaller. This meant that manufacturing technologies also had to evolve accordingly, bringing us again to fiber lasers as tools for cutting and marking of tiny electrical components. The speed with which fiber lasers run is also instrumental in allowing the electronic industry to keep up with a demand that seemingly never stops growing.
One area in which lasers are heavily used in the electronic industry is in the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs). These are boards that provide mechanical support for various electrical components while also allowing them to be connected electrically. PCBs are found in just about any electronic device.
Lasers play a role in the etching of the insulated coating on the surface of PCBs so that the conductive copper material can be exposed. These lines are extremely thin. The accuracy of both size and location of the conductive lines are instrumental in making sure that the PCB fulfills its intended purpose. Fiber lasers have proven to be the ideal tool for keeping up with these high-reliability standards.
Industrial sensors

Fiber lasers aren’t just used as tools for cutting or engraving in industrial settings. A lot of the sensors that give way to automated systems rely on lasers, typically as a means of detecting the position of a valve or motor. The challenge of industrial environments is that they are typically inhospitable for standard electrical devices – there are a lot of vibrations, extremes in temperature, and humidity close to the point of saturation.
The advantage of a laser housed in an optic fiber is it’s robust enough to endure these conditions. After all, optic fiber technology has advanced to the point where they can be submerged in the bottom of the ocean and work perfectly for dozens of years.
Final thoughts
Fiber lasers are considered the new kid on the block when it comes to industrial laser technology. Compared to older solid-state or gas-based lasers, fiber lasers do just about everything better. They are more robust, more powerful, and have a lower cost of ownership.
Given these advantages, what’s keeping companies from making the transition to fiber lasers? It’s mostly because of how long CO2 and other older lasers have been around, making it costly for manufacturing facilities to make an upgrade. Still, change is inevitable. In a few years, we expect more and more manufacturers to make the shift to fiber lasers.

