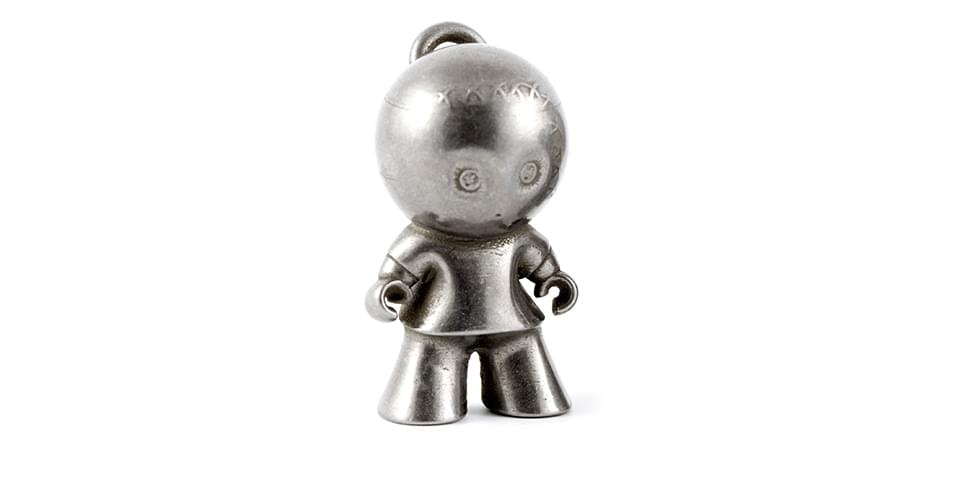
Metal 3D Printing Services: What Is It and Top 5 Options
Desktop-scale 3D printing has already proven to be a disruptive technology. From rapid prototyping to home-made crafts, 3D printing has made it easier to turn ideas into reality. However, desktop-scale 3D printing has one major limitation – it uses only plastic materials.
For other industrial and commercial applications, the use of metal for 3D printing can prove to be an invaluable step forward. After all, there are a lot of industries that rely on metal processing. Fortunately for these industries, there are now several companies that offer metal 3D printing services. How does metal 3D printing work and what are the best services available today?
How does metal 3D printing work?
The goal of metal 3D printing is the same as all other forms of 3D printing – to turn a 3D model into a real-life object. There are several techniques for metal 3D printing, but they all use raw material in the form of metal powder.
The appropriate technique will depend on the type of metal to be used, the desired characteristics of the finished product, and the budget available for the process. Here are some of the most common technologies used for metal 3D printing:
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Selective laser melting (SLM) is one of the most basic methods of metal 3D printing. The term is often used interchangeably with direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) but the two techniques have slight differences. As its name implies, SLM uses a laser to melt the metal powder, fusing them together to form complex geometries.
The key characteristic of SLM is that it fully melts the metal to achieve fusion. This makes the method more suitable for pure metals rather than metal alloys. This also means that the SLM method uses more energy than other metal 3D printing technologies. However, SLM also produces metal parts that are stronger than those produced by sintering.
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS)
DMLS is very similar to SLM in that it uses the same material (metal powder) and the same energy source (a laser). The difference is that the goal of DMSL is merely the sintering of the metals or heating of the metal particles only to the point where their surfaces weld together. This means that the energy input in DMSL is lower and that it can be used for metal alloys.
The difference between sintering and melting has pronounced effects on the quality of the finished product. Melting bonds the metal particles at the molecular level, filling in all the gaps and creating a stronger product. On the other hand, the relatively quick and energy-efficient process of sintering creates metal products with significant and uncontrolled porosity, which means they are lighter and weaker.
Electron beam melting (EBM)
In electron beam melting (EBM), an electron beam acts as the energy delivery system for melting the metal powder and achieving fusion. A distinguishing characteristic of an electron beam is that it can be separated to deliver energy to several points in a single layer of metal powder, making it a much faster process compared to those that use lasers.
One major flaw of EBM is the fact that electron beams are typically larger than laser beams, limiting the resolution of finished metal products. EBM machines are also much less common than laser machines, so there aren’t many options out there for manufacturing companies.
Multi-jet Fusion (MJF)
The rarest technology for metal 3D printing, multi-jet fusion (MJF) injects a liquid binding agent onto a bed of metal powder to bind the metal particles together. The most popular 3D printer that uses this technology is HP’s Metal Jet printer. This printer uses a thermal inkjet to introduce the binding agent to the powder via 5,280 ultra-fine nozzles.
While the binding agent is in contact with the metal powder, it promotes the absorption of infrared energy. This promotes the binding of the metal powder. However, these parts are still considered “green” and will still need to go through secondary curing and sintering processes to develop strength.
MJF is still a relatively young technology, but it has a lot of potential. In terms of versatility, using different binding agents may be the key to achieving different characteristics in the finished metal products. It can also deliver a level of detail that is at par or slightly better than what laser-based methods are capable of.
Top 5 metal 3D printing services
1. Sculpteo

Sculpteo is usually one of the first choices when it comes to any type of 3D printing and rapid prototyping service. With several facilities in the US and Europe, they serve a huge market and has one of the widest range of offerings in terms of materials and 3D printing technologies.
If you’re just interested in metals, then you’ll be glad to know the Sculpteo offers DMLS, SLM, and Binder Jetting technologies. They can work with aluminum, stainless steel, metal steel, and titanium. They also offer wax casting services if you need a finished part made with silver, bronze, or brass.
One of our favorite things about working with Sculpteo is the array of value-added services that they provide. On top of 3D printing, they can also do laser engraving to add a touch of personalization to your printed parts. They also have a 3D design service that can help you touch up and enhance your 3D models to make them more appropriate for additive manufacturing. They even provide training via Sculpteo Studio, their approved training organization.
To be fair, there are other 3D printing services with a wider range of services than Sculpteo. However, there’s no doubt that Sculpteo offers seamless customer experience and high-quality performance.
2. Stratasys

The 3D metal printing technologies of Stratasys may be limited to DMLS, but they make up for it with a wider range of materials. Right now, they can work with aluminum, copper, cobalt chrome, stainless steel, titanium, and nickel alloy. If you need CNC machining services, they also offer it for stainless steel and aluminum.
The company’s Material Wizard page is an excellent free resource for comparing all the physical and chemical characteristics of the materials for which they offer 3D printing services. This is an incredibly useful tool for industrial and commercial customers that condenses several days’ worth of material research into an easy-to-use interface.
While Stratasys doesn’t provide a software platform or web interface for customers who want to submit and review their 3D models, they do offer design services. These services range from modeling for those who don’t have existing 3D models, to modification of models to make them more appropriate both for additive manufacturing and for the customer’s needs.
On top of metal 3D printing, Stratasys also offers 3D printing services for industrial plastics like Nylon, polycarbonate, ABS, and ULTEM resin. They can do this via FDM, SLS, or SLA technologies. If expertise is what you’re looking for, then you can’t go wrong with Stratasys.
3. Shapeways

US-based Shapeways has a fairly limited portfolio as far as metal 3D printing services are concerned. They offer SLM for aluminum and Binder Jetting for stainless steel and metal steel. If you need parts done in copper, bronze, brass, or silver, they can also do those for you but using a more traditional wax casting method.
What we like about Shapeways is how they have streamlined the ordering process. Leveraging on their “3D design as a service” model, their online ordering process goes through a 3D design platform provided by Zverse. Using the online platform, customers can simply upload their 3D models and the software will automatically check for errors and propose repairs.
Once the model has been cleared for printing, the customer is presented with options for the different materials and types of finish. A quote is then provided based on the specs provided by the customer, and the manufacturing process can proceed once the customer has agreed.
By going the extra mile to improve the customer experience, Shapeways has been able to offer a compelling choice to both commercial and industrial customers. Right now, the company seems more focused on its plastic-based 3D printing services, so you might want to take a look at those if you need anything done in Nylon or TPU.
4. 3D Hubs

The model of 3D Hubs is quite different from the other companies in this list, as they act as a platform for connecting customers to a vast network of manufacturing platforms. This means that they cast a pretty wide net. This is a good thing for global customers who find it difficult to get in touch with manufacturers nearby who offer 3D printing services.
The biggest drawback is that 3D Hubs hasn’t quite developed a robust list of metal 3D printing services yet. Right now, they only offer 3D printing services for aluminum and stainless steel, although the actual technology to be used (either DMLS, SLM, or Binder Jetting) will depend on which manufacturing company will serve the orders.
The strength of 3D Hubs is that their other manufacturing technologies are extremely well-developed. They offer CNC machining services for a very wide range of both metals and plastics. They also offer sheet metal and injection molding services. For those who need huge volumes of parts, the partners of 3D Hubs can provide part marking and surface finishing services. If you’re looking for a company that offers more than 3D printing, then 3DHubs certainly fits the bill.
5. i.Materialise
i.Materialise has managed to build a solid reputation for its 3D printing and manufacturing services through the years, serving customers from industries like jewelry making and healthcare. Right now, they offer DMLS and SLS services for both aluminum and titanium. They can also work with steel and stainless steel using a Binder Jetting technique.
If you need parts done in precious metals like gold, silver, copper, or brass, they can manufacture those using a lost wax casting technique. This is a somewhat indirect use of 3D printing, but it can still deliver the same level of resolution and customization. Lost wax casting is an excellent 3D printing alternative for creating custom jewelry pieces.
i.Materialise is a model of transparency, customer communication, and professionalism. At the onset, they will let a customer know if there’s a startup cost involved in printing their model, the maximum build volume for the chosen material, and their estimated lead times. They also offer discounts for bulk orders. Customers can upload their 3D models directly via the website and receive tips on how the models can be improved or repaired.
For those are unsure about how the different materials look or feel, i.Materialise can provide sample kits of various 3D printed parts. These kits are very inexpensive and can be very useful in managing the expectations of customers.
Final thoughts
Making the jump from 3D printing with plastics to 3D printing with metals is a huge upgrade that requires much more sophisticated equipment. While this kind of technology still remains inaccessible price-wise, customers can take advantage of companies that offer metal 3D printing services.
The advantage of going to a metal 3D printing service is that you won’t need to make a huge investment in the equipment and you can be confident that your job is being handled by experts in the field. All of the five recommendations we have listed here have been in the business for a long time and have gained the trust of a lot of customers.

