Part 107 Test Questions
The Part 107 drone license, or remote pilot certificate, is a requirement imposed by the FAA for remote pilots who want to use their drones for commercial operations. One of the most important steps in the whole process of getting a drone license is taking and passing the Part 107 knowledge test. Studying for this knowledge test is no small feat – you will need knowledge on FAA regulations, chart reading, radio communication, weather, emergency procedures, and drone maintenance.
As part of our effort to aid aspiring commercial drone pilots in their preparations for the knowledge test, we have compiled a list of sample test questions on each topic. We also give you a breakdown of how the topics are distributed throughout the test so you will know which ones to prioritize while you are studying.
Breaking it Down
The Part 107 knowledge test is composed of 60 multiple choice questions, of which you need to correctly answer 70% to pass. Based on accounts from people who have taken the test, the questions are roughly distributed according to the topics as illustrated below:
| Topic | Percentage of Items on Test |
|---|---|
| Aircraft Operations | 35 – 45% |
| Regulations | 15 – 25% |
| Airspace and Requirements | 15 – 25% |
| Weather | 11 – 16% |
| Loading and Performance | 7 – 11% |
Questions on aircraft or drone operations take up a third to almost half of all the questions in the knowledge test. This is followed by questions on both FAA regulations, and Airspace Classifications and their corresponding requirements. Finally, questions on weather (reports, forecasts) and how loading and other factors affect aircraft performance are the least-represented.
You may use this handy guide to help you allocate the time you spend on each topic while you are preparing for the test. Of course, it would still be in your best interest to develop a working level of knowledge on each of the topics listed above, as they are all essential in your growth as a drone pilot. Being well-versed on each topic is probably the most foolproof method for you to pass the test, regardless of how each topic is represented.
That being said, we have compiled in the next sections several sample Part 107 test questions to help you determine the most common topics that you need to study. You may either use these questions as study guides, or as a practice test to see if you are ready to take on the real thing. Many of these questions come from the FAA.
Aircraft Operations
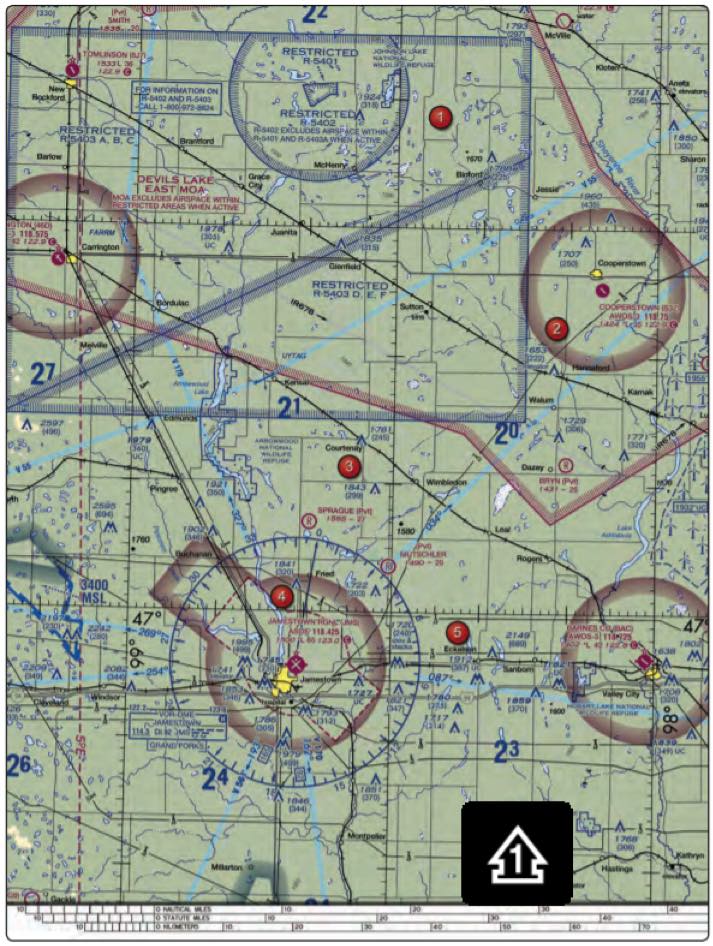
1. (Refer to figure above, area 4) What does the line of latitude at area 4 measure?
- The degrees of latitude east and west of the Prime Meridian.
- The degrees of latitude north and south from the equator.
- The degrees of latitude east and west of the line that passes through Greenwich, England.
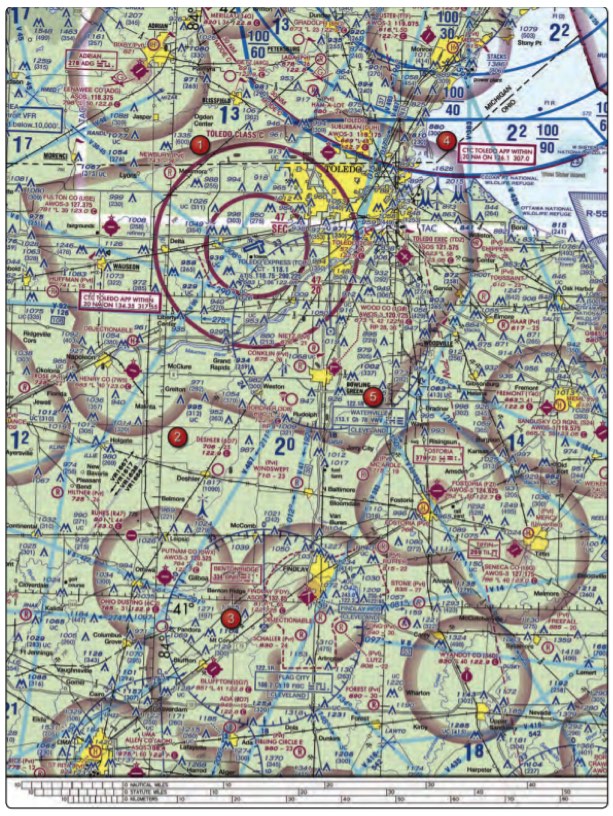
1. (Refer to figure above, area 2) The chart shows a gray line with “VR1667, VR1617, VR1638, and VR1668.” Could this area present a hazard to the operations of a small UA?
- No, all operations will be above 400 feet.
- Yes, this is a Military Training Route from 1,500 feet AGL.
- Yes, the defined route provides traffic separation to manned aircraft.
3. Which technique should a pilot use to scan for traffic?
- Concentrate on relative movement detected in the peripheral vision area.
- Systematically focus on different segments of the sky for short intervals.
- Continuous sweeping of the windshield from right to left.
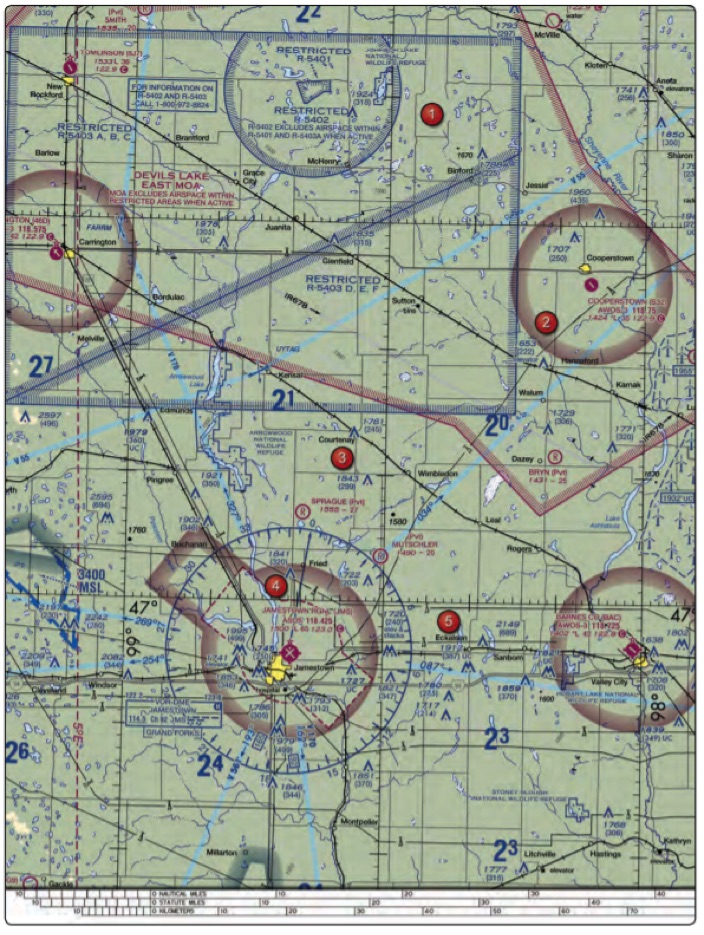
4. (Refer to figure above, Area 2) What is the approximate latitude and longitude of Cooperstown Airport?
- 47º55’N – 98º06’W
- 47º25’N – 99º54’W
- 47°25’N – 98°06’W
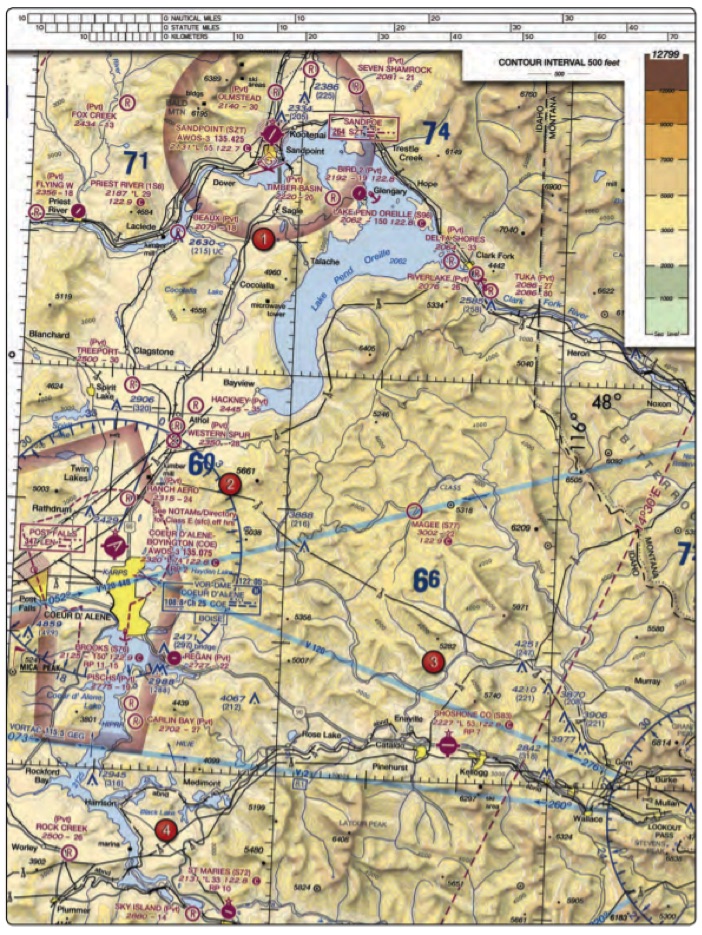
5. (Refer to figure above, area 2) At Coeur D’Alene which frequency should be used as a Common Traffic Advisory Frequency (CTAF) to monitor airport traffic?
- 122.8 MHz.
- 135.075 MHz.
- 122.05 MHz.
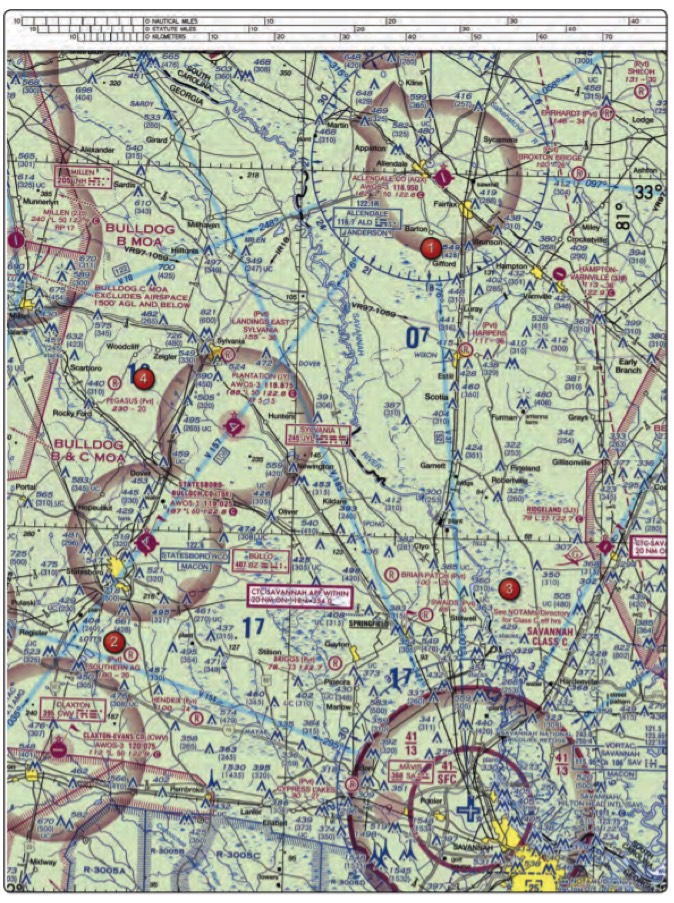
6. (Refer to figure above, area 3.) What is the height of the lighted obstacle approximately 6 nautical miles southwest of Savannah International?
- 1,498 feet MSL.
- 1,531 feet AGL.
- 1,548 feet MSL.
7. To avoid striking guy wires, how far from a skeletal tower shoud you operate your aircraft?
- 2000 feet
- 1000 feet
- 500 feet
FAA Regulations
1. According to 14 CFR part 107 the remote pilot in command (PIC) of a small unmanned aircraft planning to operate within Class C airspace
- Must use a visual observer.
- Is required to file a flight plan.
- Is required to receive ATC authorization.
2. In accordance with 14 CFR part 107, you may operate an sUAS from a moving vehicle when no property is carried for compensation or hire:
- Over a sparsely populated area.
- Over suburban areas.
- Over a parade or other social events.
3. According to 14 CFR part 48, when must a person register a small UA with the Federal Aviation Administration?
- When the small UA is used for any purpose other than as a model aircraft.
- Only when the operator will be paid for commercial services.
- All civilian small UAs weighing greater than .55 pounds must be registered regardless of its intended use.
4. While operating a small unmanned aircraft system (sUAS), you experience a flyaway and several people suffer injuries. Which of the following injuries requires reporting to the FAA?
- Scrapes and cuts bandaged on site
- Minor bruises
- An injury requiring a hospitalization over 48 hours
5. When requesting a waiver, the required documents should be presented to the FAA at least how many days prior to the planned operation?
- 90 days
- 10 days
- 30 days
6. After receiving a part 107 remote pilot certificate with an sUAS rating, how often must you satisfy recurrent training requirements?
- Every 36 months
- Every 12 months
- Every 24 months
Airspace and Requirements

1. (Refer to figure above, Area 3) The vertical limits of that portion of Class E airspace designated as a Federal Airway over Magee Airport are:
- 700 feet MSL to 12,500 feet MSL.
- 7,500 feet MSL to 17,999 feet MSL.
- 1,200 feet AGL to 17,999 feet MSL.
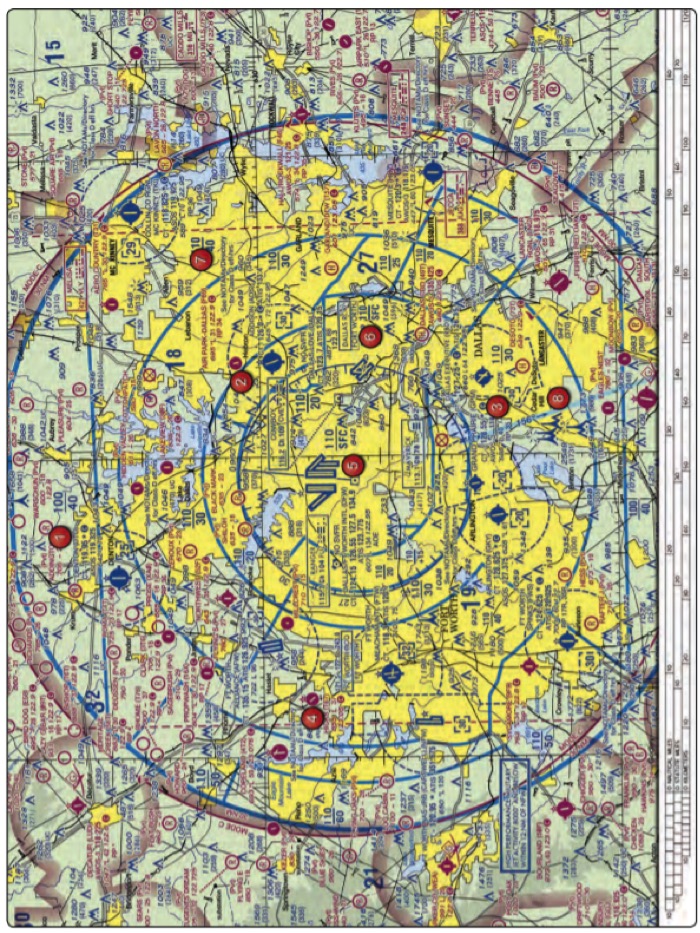
2. (Refer to figure above, area 2) The floor of Class B airspace at Addison Airport is
- 2,500 feet MSL
- At the surface
- 3,000 feet MSL
3. Outside control tower hours, class D airspace is:
- A. Class G
- B. Unchanged
- C. Class E
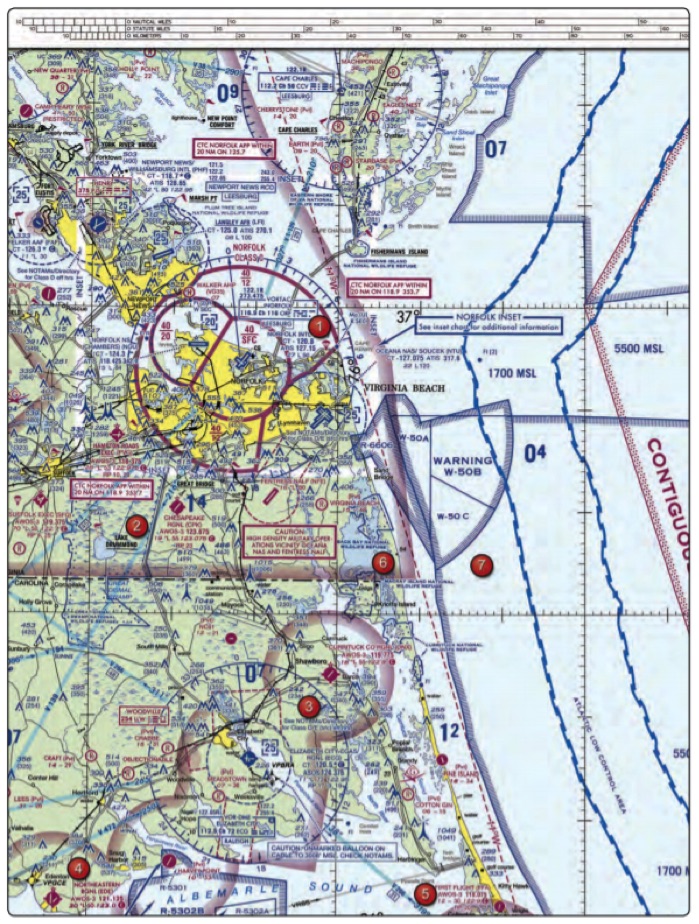
4. (Refer to figure above, area 4) What hazards to aircraft may exist in restricted areas such as R-5302B?
- Military training activities that necessitate acrobatic or abrupt flight maneuvers.
- Unusual, often invisible, hazards such as aerial gunnery or guided missiles.
- High volume of pilot training or an unusual type of aerial activity.
5. According to 14 CFR part 107, how may a remote pilot operate an unmanned aircraft in class C airspace?
- The remote pilot must contact the Air Traffic Control (ATC) facility after launching the unmanned aircraft.
- The remote pilot must monitor the Air Traffic Control (ATC) frequency from launch to recovery.
- The remote pilot must have prior authorization from the Air Traffic Control (ATC) facility having jurisdiction over that airspace.

6. (Refer to figure above, area 3) With ATC authorization, you are operating your small unmanned aircraft approximately 4 SM southeast of Elizabeth City Regional Airport (ECG). What hazard is indicated to be in that area?
- Unmarked balloon on a cable up to 3,008 feet MSL.
- Unmarked balloon on a cable up to 3,008 feet AGL.
- High density military operations in the vicinity.
Weather
1. Clouds are divided into four families according to their
- A. Outward shape.
- B. Height range.
- C. Composition.
2. What are characteristics of a moist, unstable air mass?
- Turbulence and showery precipitation.
- Poor visibility and smooth air.
- Haze and smoke.
3. You have received an outlook briefing from flight service through 1800wxbrief.com. The briefing indicates you can expect a low-level temperature inversion with high relative humidity. What weather conditions would you expect?
- Smooth air, poor visibility, fog, haze, or low clouds.
- Light wind shear, poor visibility, haze, and light rain.
- Turbulent air, poor visibility, fog, low stratus type clouds, and showery precipitation.
4. Which of the following is considered a “ceiling”?
- Fog, mist or haze.
- Any cloud below 1,000 ft AGL
- A broken or overcast cloud layer
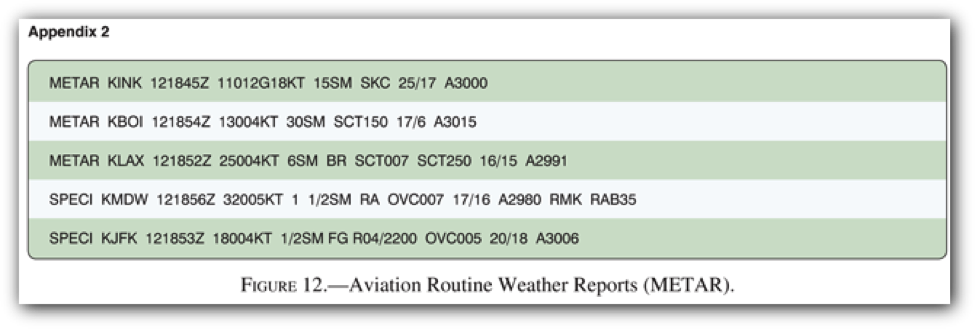
5. (Refer to figure above) What are the current conditions for Chicago Midway Airport (KMDW)?
- A. Sky 700 feet overcast, visibility 1-1/2SM, rain.
- B. Sky 7000 feet overcast, visibility 1-1/2SM, heavy rain.
- C. Sky 700 feet overcast, visibility 11, occasionally 2SM, with rain.
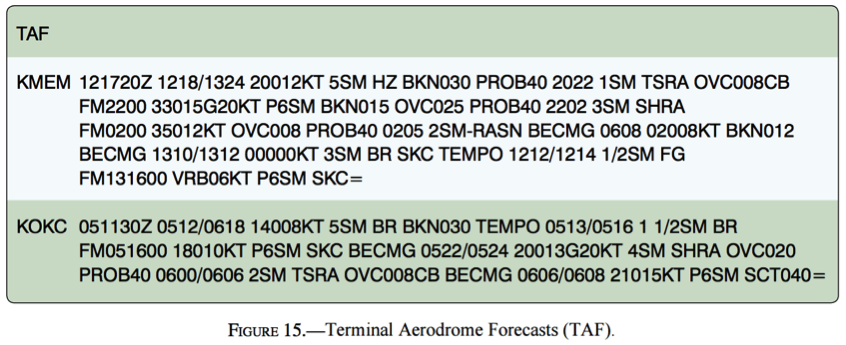
6. (Refer to figure above) What is the valid period for the TAF for KMEM?
- 1700Z to 2000Z
- 2200Z to 1600Z
- 1800Z to 2400Z
Loading and Performance
1. Which combination of atmospheric conditions will reduce aircraft takeoff and climb performance?
- Low temperature, low relative humidity, and low density altitude.
- High temperature, low relative humidity, and low density altitude.
- High temperature, high relative humidity, and high density altitude.
2. Which basic flight maneuver increases the load factor on an airplane as compared to straight-and-level flight?
- Climbs.
- Turns.
- Stalls.
3. Which is true regarding the presence of alcohol within the human body?
- A small amount of alcohol increases vision acuity.
- Consuming an equal amount of water will increase the destruction of alcohol and alleviate a hangover.
- Judgment and decision-making abilities can be adversely affected by even small amounts of alcohol.
4. What effect does high density altitude have on the efficiency of a UA propeller?
- Propeller efficiency is increased.
- Propeller efficiency is decreased.
- Density altitude does not affect propeller efficiency.
5. How often is the Remote PIC required to inspect the sUAS to ensure that it is in a condition for safe operation?
- Monthly
- Before each flight
- Annually
6. When operating an unmanned airplane, the remote pilot should consider that the load factor on the wings may be increased anytime:
- The CG is shifted rearward to the aft CG limit
- The airplane is subjected to maneuvers other than straight and level flight.
- The gross weight is reduced
A final word: How NOT to use this study guide
This guide only shows a smattering of the knowledge that you will need in order to pass the Part 107 knowledge test. What we provided here are only sample questions. Expect the actual test questions to be considerably different, so it will do you no good to memorize the answers to our sample questions. In fact, the test questions in the actual test will be picked from a pool of questions developed by the FAA, so no two exams will be similar.
It is more important to develop the proficiency needed to answer these questions, so you’ll be better prepared for your Part 107 knowledge test.


